
In case you’re still interested, here is a link on how to do it: Important Points to Note

Unfortunately, the procedure is complicated, and you should use it at your own risk. But you can deactivate the encryption to simplify its functionality and reduce CPU cycles. The data stored in the ReadyBoost cache is safe, as it is protected using the 128-bit AES encryption standard by default. So, when your Windows 10 needs to access frequently used files, it fetches it from the disk drive instead of the RAM. In any case, RAM is what influences the system speed. When you launch ReadyBoost, Windows 10 uses your flash drive’s memory as RAM. For example, the cache could be application files, system files, and user documents. This program works in conjunction with SuperFetch, a service that uses an algorithm to decide which files should be kept in the cache. How Does It Improve Windows 10 Performance? Thankfully, this utility actually does work in Windows 7, 8, and 10. But, to be honest, the claims fell flat for most of us. Microsoft first introduced ReadyBoost in 2007 with the promise of accelerating the performance of Windows Vista. It stores this cached data on your removable devices, such as flash drives, CompactFlash memory cards, and Secure Digital.
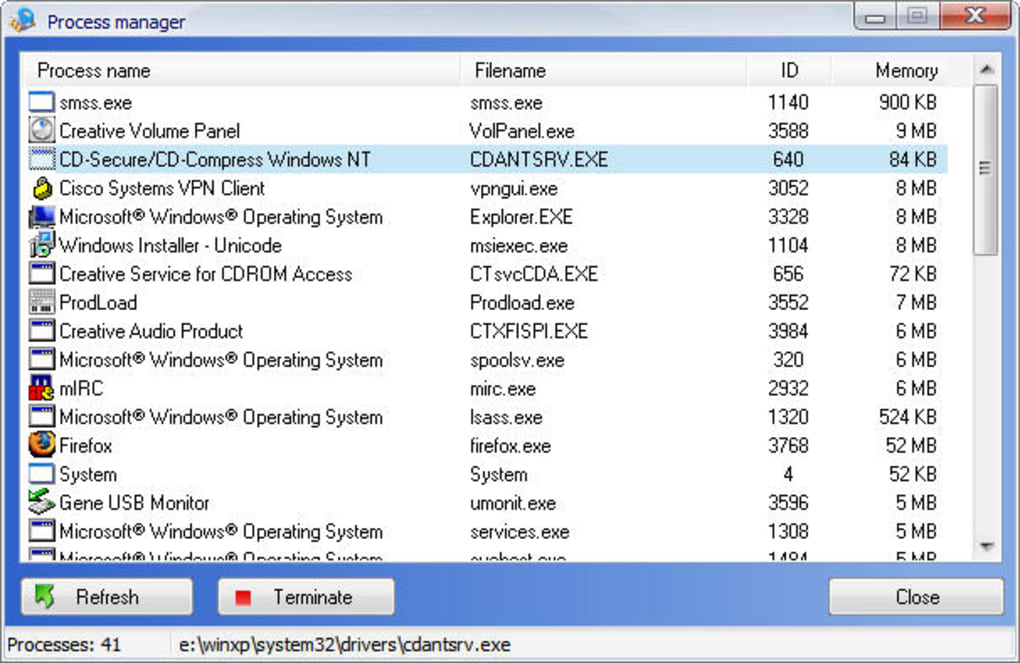
ReadyBoost is a Windows program that caches frequently used files. If you have not heard of ReadyBoost or how to use it, this guide will help you get the most out of this Windows utility. But you should know that this feature is not available for all systems. I usually use this service to make my family members’ old computers or laptops faster by inserting a flash drive or a memory card and activating ReadyBoost. It utilizes free space on fast removable devices to augment system memory.
ReadyBoost is a little-known Microsoft technology created way back for Vista and was included in newer versions of Windows.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
